pygmt.Figure.solar
- Figure.solar(terminator='day_night', terminator_datetime=None, fill=None, pen=None, projection=None, region=None, verbose=False, panel=False, transparency=None, **kwargs)
Plot day-night terminators and other sunlight parameters.
This method plots the day-night terminator. Alternatively, it can plot the terminators for civil twilight, nautical twilight, or astronomical twilight.
Full GMT docs at https://docs.generic-mapping-tools.org/6.6/solar.html.
Aliases:
B = frame
p = perspective
G = fill
J = projection
R = region
T = terminator, +d/+z: terminator_datetime
V = verbose
W = pen
c = panel
t = transparency
- Parameters:
terminator (
Literal['astronomical','civil','day_night','nautical'], default:'day_night') –Set the type of terminator. Choose one of the following:
"astronomical": Astronomical twilight"civil": Civil twilight"day_night": Day-night terminator"nautical": Nautical twilight
Refer to https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Twilight for the definitions of different types of twilight.
terminator_datetime (str or datetime object) – Set the date and time for the terminator calculation. It can be provided as a string or any datetime-like object recognized by
pandas.to_datetime. The time can be specified in UTC or using a UTC offset. The offset must be an integer number of hours (e.g., -8 or +5); fractional hours are truncated towards zero (e.g., -8.5 becomes -8 and +5.5 becomes +5). [Default is the current UTC date and time].region (str or list) – xmin/xmax/ymin/ymax[+r][+uunit]. Specify the region of interest.
projection (
str|None, default:None) – projcode[projparams/]width|scale. Select map projection.frame (bool, str, or list) – Set map boundary frame and axes attributes.
fill (
str|None, default:None) – Set color or pattern for filling terminators [Default is no fill].pen (
str|None, default:None) – Set pen attributes for lines [Default is"0.25p,black,solid"].verbose (bool or str) – Select verbosity level [Full usage].
panel (
int|tuple[int,int] |bool, default:False) –Select a specific subplot panel. Only allowed when used in
Figure.subplotmode.Trueto advance to the next panel in the selected order.index to specify the index of the desired panel.
(row, col) to specify the row and column of the desired panel.
The panel order is determined by the
Figure.subplotmethod. row, col and index all start at 0.perspective (list or str) – [x|y|z]azim[/elev[/zlevel]][+wlon0/lat0[/z0]][+vx0/y0]. Select perspective view and set the azimuth and elevation angle of the viewpoint [Default is
[180, 90]]. Full documentation is at https://docs.generic-mapping-tools.org/6.6/gmt.html#perspective-full.transparency (float) – Set transparency level, in [0-100] percent range [Default is
0, i.e., opaque]. Only visible when PDF or raster format output is selected. Only the PNG format selection adds a transparency layer in the image (for further processing).
Example
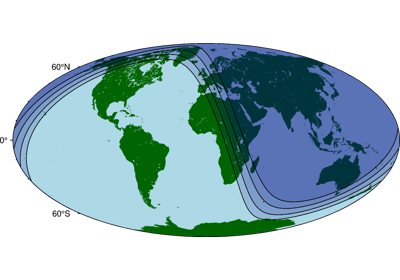
>>> # import the Python module "datetime" >>> import datetime >>> import pygmt >>> # create a datetime object at 8:52:18 on June 24, 1997 (time in UTC) >>> date = datetime.datetime( ... year=1997, month=6, day=24, hour=8, minute=52, second=18 ... ) >>> # create a new plot with pygmt.Figure() >>> fig = pygmt.Figure() >>> # create a map of the Earth with the coast method >>> fig.coast(land="darkgreen", water="lightblue", projection="W10c", region="d") >>> fig.solar( ... # set the terminator to "day_night" ... terminator="day_night", ... # pass the datetime object ... terminator_datetime=date, ... # fill the night-section with navyblue at 75% transparency ... fill="navyblue@75", ... # draw the terminator with a 1-point black line ... pen="1p,black", ... ) >>> # show the plot >>> fig.show()